Living Planet Report shows a dramatic decline in freshwater species - giving more urgency to implement Emergency Recovery Plan
A key element of the 2020 Living Planet Report's Freshwater Deep Dive, this scientific paper outlines a revolutionary plan to reverse the rapid decline in the world’s freshwater species and habitats while protecting our life support systems.

With biodiversity vanishing from rivers, lakes and wetlands at alarming speed, the Emergency Recovery Plan sets out how we can reverse the rapid decline in the world’s freshwater species and habitats – and safeguard our life support systems. A key element of the 2020 Living Planet Report's Freshwater Deep Dive, the Recovery Plan gives us a framework from which we can push for greater freshwater representation in the new CBD Post-2020 targets.
Published in BioScience, the Emergency Recovery Plan calls for the world to take urgent steps to tackle the threats that have led the 84% collapse in freshwater biodiversity and the degradation of 90% of the world’s wetlands reported in the 2020 Living Planet Index report – ecosystems that provide us with water, food, livelihoods, and protection from floods, droughts and storms.
Developed by a global team of scientists from WWT, WWF, International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Conservation International, the University of Cardiff and other eminent organisations and academic institutions, this is the first comprehensive plan to protect and restore freshwater habitats, which host more species per square kilometre than land or oceans – and are losing this extraordinary biodiversity two or three times faster.
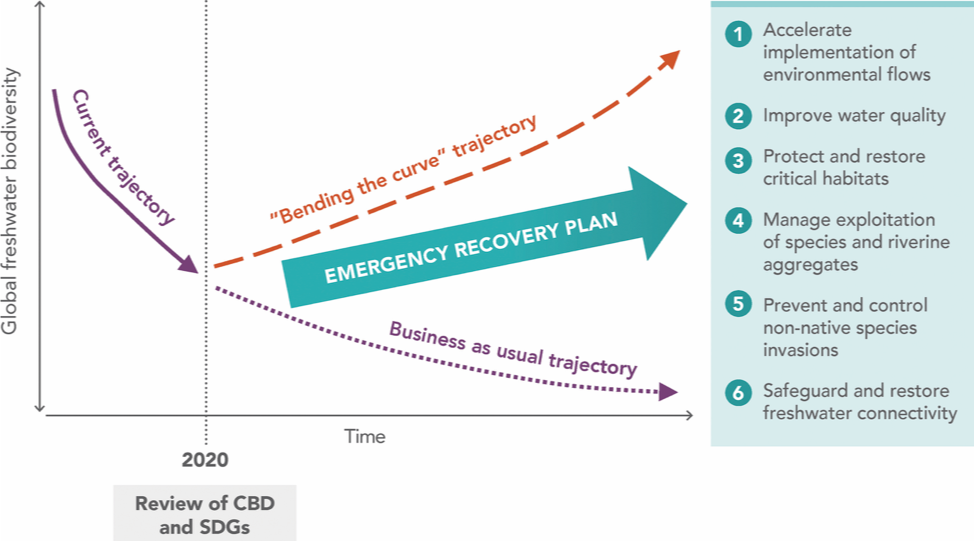
The six-point plan prioritises solutions that are rooted in cutting edge science and have already proven successful in certain locations:
- Letting rivers flow more naturally
- Reducing pollution
- Protecting critical wetland habitats
- Ending overfishing and unsustainable sand mining in rivers and lakes
- Controlling invasive species
- Safeguarding and restoring river connectivity through better planning of dams and other infrastructure
WWT's Director of Conservation Dr James Robinson said:
Our newly published Emergency Recovery Plan presents an outline of straightforward and pragmatic solutions to the freshwater biodiversity crisis that are already proven to work. A strategic approach to the implementation of these measures is vital if we are to make a global impact.
Wetlands are natural super systems that sustain an extraordinary level of biodiversity. We must act now to protect them.
Critically, with governments meeting in November to agree on a new global deal to conserve and restore biodiversity at a landmark conference of the Convention on Biological Diversity, the authors recommend some new targets, including on restoring water flows, controlling illegal and unregulated sand mining in rivers, and improving management of freshwater fisheries that feed hundreds of millions of people.
Nowhere is the biodiversity crisis more acute than in the world’s rivers, lakes and wetlands – with over a quarter of freshwater species now heading for extinction.
The Emergency Recovery Plan can halt this decades-long decline and restore life to our dying freshwater ecosystems, which underpin all of our societies and economies.
Dave Tickner, WWF-UK Chief Freshwater Advisor and lead author on the paper
Covering approximately 1% of the Earth’s surface, rivers, lakes and freshwater wetlands are home to 10% of all species and more described fish species than in all the world’s oceans. But they are rapidly disappearing with populations of freshwater megafauna – such as river dolphins, sturgeon, beavers, crocodiles and giant turtles – crashing by 88% in the past half century.
The causes of the global collapse in freshwater biodiversity are no secret, yet the world has consistently failed to act, turning a blind eye to the worsening crisis even though healthy freshwater ecosystems are central to our survival.
The Emergency Recovery Plan provides an ambitious roadmap to safeguarding freshwater biodiversity – and all the benefits it provides to people across the world.
Co-author, Professor Steven Cooke of Carleton University in Canada
The Emergency Recovery Plan highlights a variety of measures that together will transform the management and health of rivers, lakes and wetlands, such as treating more than 20% of sewage before it is flushed into nature, avoiding dams on the world’s remaining free flowing rivers, and expanding and strengthening protected areas in partnership with local communities.
All the solutions in the Emergency Recovery Plan have been tried and tested somewhere in the world: they are realistic, pragmatic and they work.
We are calling on governments, investors, companies and communities to prioritise freshwater biodiversity – often neglected by the conservation and water management worlds. Now is the time to implement these solutions, before it is too late.
James Dalton, Director of IUCN’s Global Water Programme
"We have the last opportunity to create a world with rivers and lakes that once again teem with wildlife, and with wetlands that are healthy enough to sustain our communities and cities, but only if we stop treating them like sewers and wastelands,” said Tickner. “This decade will be critical for freshwater biodiversity: countries must seize the chance to keep our life support systems running by ensuringfreshwater conservation and restoration are central to a New Deal for Nature and People.”
Find out more about the recovery plan



